
Designing Interactives

Interactive Object
Object Physics
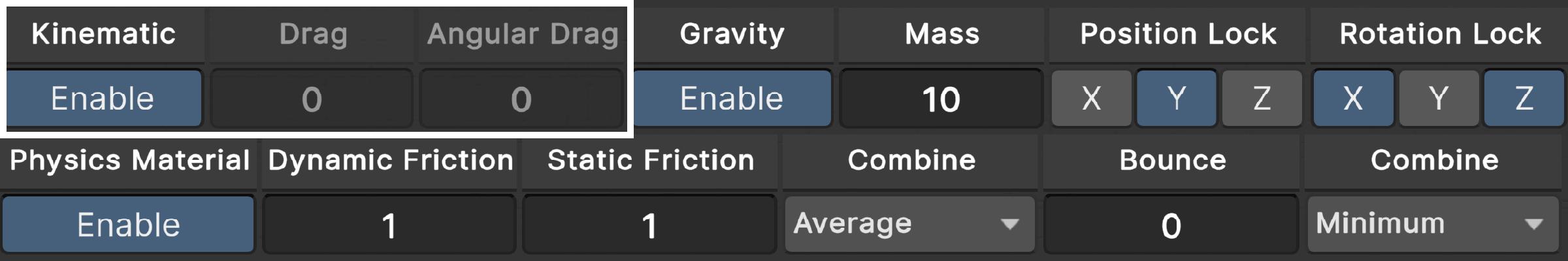
Kinematic
Toggle between physics-based and kinematic movement for the GameObject. When Kinematic is enabled, the physics system will not apply forces to move or rotate the GameObject, instead, the object's motion can only be controlled by Motion Actions and Motion Controllers.
The above description has been paraphrased from the Unity 6.1 Rigidbody component reference documentation pageDrag
Define the decay rate of a objects linear velocity, to simulate drag, air resistance, or friction. Low values produce a slower decay rate, so that the object moves faster for longer (this is useful for simulating heavy real-world objects). High values produce a faster decay rate, so that the object slows down over a short amount of time (this is useful for simulating lightweight real-world objects).
The above description has been paraphrased from the Unity 6.1 Rigidbody component reference documentation pageAngular Drag
Define the decay rate of a object’s rotational velocity, to simulate drag, air resistance, or friction. Low values produce a slower decay rate, so that the object moves faster for longer (this is useful for simulating heavy real-world objects). High values produce a faster decay rate, so that the object slows down over a short amount of time (this is useful for simulating lightweight real-world objects). Note that you cannot make the object stop rotating just by setting its Angular Drag to infinity.
The above description has been paraphrased from the Unity 6.1 Rigidbody component reference documentation page